Natural Gas
Bringing the Heat
In a Flash

Natural gas can be converted into other forms of energy such as light and heat.
Natural gas
Natural gas is a non-renewable fossil fuel formed from the remains of tiny sea plants and animals that died 300-400 million years ago. Approximately 90% of natural gas is composed of methane, but it also contains other gases such as propane and butane.
Burning Questions
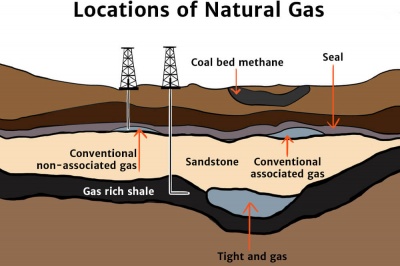
How is natural gas formed?
300-400 million years ago, the remains of tiny sea plants and animals sank to the bottom of the oceans, where they were buried by sediment that turned into rock.
Over the years, the layers of rock became thousands of feet thick, putting the energy-rich plant and animal matter under a lot of pressure. Eventually, the pressure and heat changed this organic mixture into oil (petroleum) and natural gas.
Natural gas became trapped in the rock layers – much like water is trapped in a wet sponge.
Natural gas is a fossil fuel trapped under rocks deep underground.
How is natural gas formed?
Natural gas can be tricky to find, as it's generally trapped in rocks located deep underground. To find natural gas deposits, geologists may:
The journey goes like this:
- Look at surface rocks to find clues about underground formations.
- Set off small explosions or drop heavy weights on the Earth's surface, in order to record the sound waves as they bounce back from the underground rock layers.
- Measure the gravitational pull of rock masses deep within the Earth.
If a site looks promising, wells may be drilled to find the natural gas deposits – as these wells average almost 9000 feet deep and can cost hundreds of dollars per foot to drill, it's important to choose natural gas sites carefully!
Are there other sources of natural gas?
Yes. Natural gas can also be found in seams of coal, called coal bed methane, as well as in the methane produced in landfills.
While natural gas is considered a non-renewable energy source, landfill gas is a renewable source of methane, as it comes from decaying rubbish.
What happens to natural gas after it comes out of the ground?
Once it's been taken from the ground, natural gas is sent to a processing plant to be cleaned of impurities and separated into its different components – this is mostly methane, as well other gases such as propane and butane.
What is propane?
Propane is a gas that comes from natural gas and petroleum (oil). It is a clean-burning fuel that has a lot of different uses, including:
- Making products and fuelling industry
- Heating barns and operating farm equipment
- Fuelling hot air balloons
- Heating homes
- Fuelling barbeques and appliances
- Fuelling machinery
What Do You Mean?

Up to 482,000km of pipeline delivers natural gas to processing plants.
Natural gas was formed from decaying sea plants and animals that sank to the bottom of the ocean when they died 300-400 million years ago.
Natural gas wells drilled to find natural gas deposits in sites identified by geologists.
Methane is the main component of natural gas, making up about 90%.
Propane is a gas derived from natural gas and petroleum (oil).
Coal bed methane is a source of natural gas found in coal seams.
Landfill gas is a renewable source of methane produced by burning decaying rubbish.
Speedy Summary

Natural gas contains methane, butane and propane.
Natural gas was formed from tiny sea plants and animals that died and fell to the bottom of the ocean 300-400 million years ago. Natural gas can be used to fuel industry and machinery, as well as for a wide variety of heating purposes.
Teacher's Toolkit
Take this to the classroom!
Curriculum ready content.