How a PV Cell Works
Sunny Side Up
In a Flash
Solar panels convert the sunlight's photon energy into electricity.
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) cells generate electricity by absorbing sunlight and using that light energy to create an electrical current. There are many PV cells within a single solar panel, and the current created by all of the cells together adds up to enough electricity to help power your school, home and businesses.
Similar to the cells in a battery, cells in a solar panel are designed to generate electricity; except a battery's cells make electricity from chemicals and a solar panel's cells generate electricity by capturing sunlight instead.
Burning Questions
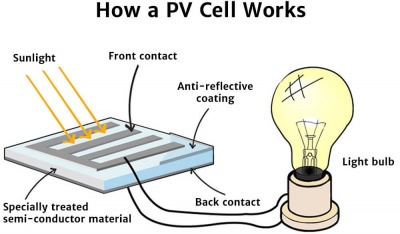
How does a PV Cell work?
Sunlight is composed of photons, or particles of radiant solar energy. These photons contain various amounts of energy depending on the wavelength of the solar spectrum.

When the photons strike a solar cell, some are absorbed while others are reflected. When the material absorbs sufficient photon energy, electrons within the solar cell material dislodge from their atoms.
The electrons migrate to the front surface of the solar cell, which is manufactured to be more receptive to the free electrons. When many electrons, each carrying a negative charge, travel toward the front surface of the cell, the resulting imbalance of charge between the cell's front and back surfaces creates a voltage potential like the negative and positive terminals of a battery. When the two surfaces are connected through an external load, electricity flows.
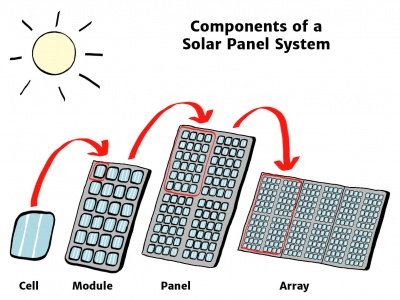
Individual solar cells vary in size from about 1 cm to about 10 cm across. A cell of this size can only produce 1 or 2 watts, which isn't enough power for most applications. To increase power output, cells are electrically connected into a module. Modules are connected to form an array. The term "array" refers to the entire generating plant, whether it is made up of one or several thousand modules.
The performance of a photovoltaic array is dependent upon sunlight. Climate (e.g. clouds, fog) has a significant effect on the amount of solar energy received by a PV array and, in turn, its performance.
What is Photovoltaic?
The word photovoltaic (PV) comes from the Greek word "photo" meaning light and the modern word "Volt" or "Voltage”, a unit of electrical potential energy (named in honour of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827),
What Do You Mean?
Large banks of solar cells maximise the amount of solar energy they can generate.
Solar photovoltaic (PV) is the generation of electricity from the sun's energy, using PV cells.
A Solar Cell is a sandwich of two different layers of silicon that have been specially treated so they will let electricity flow through them in a specific way.
A Solar Panel is made up of many solar cells.
A Solar array is a collection of multiple solar panels that generate electricity as a system.
Speedy Summary

Large banks of solar cells maximise the amount of solar energy they can generate.
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) cells generate electricity by absorbing sunlight and using that light energy to create an electrical current.
Teacher's Toolkit
Take this to the classroom!
Curriculum ready content.